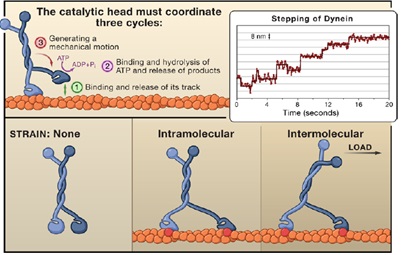
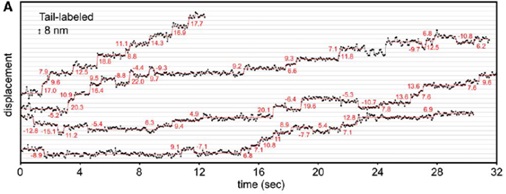
In vivo, molecular motors are involved in a range of important life activities such as muscle contraction, cytoplasmic transport, DNA transcription, and mitosis. In performing the above functions, the molecular motor needs to complete the specific trajectory on the cytoskeleton by means of the energy released by ATP hydrolysis. Therefore, the research on the walking mechanism of molecular motor along the cytoskeleton is of great significance for understanding the mechanism of action of molecular motors and the diagnosis and treatment of related diseases. Ronald D. Vale, a research group at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute in the United States, used single-molecule fluorescent labeling and tracing techniques to reveal the walking properties of one of the molecular motors, Dynein, on the microtubule skeleton (Figure 1 ). Ronald D. Vale et al. constructed a fusion protein expression vector of dynein and HaloTag, which was expressed by budding yeast and added HaloTag biotin ligand to the purified fusion protein to obtain biotinylated dynein. In order to label streptavidin-Quantum dots (SA-QDs) coupled with streptavidin, the biotinylated dynein was placed in an in vitro reaction cell, first with axon in the absence of ATP (axonemes) ) Combine and incubate with SA-QDs. After the above reaction, the dynein is labeled by quantum dots while avoiding the accumulation of dynein by SA-QDs. Using the above quantum dot-labeled dynein, the researchers used high-sensitivity and high-resolution fluorescence imaging techniques to analyze the step-behavior properties of dynein on the microtubule skeleton (Figure 2). The high fluorescence brightness and photobleaching resistance of quantum dots can meet the requirements of precise tracer; at the same time, the high fluorescence stability of quantum dots can make the tracer duration last for several minutes. Data analysis showed that the quantum dot marking of the head and tail of the dynein did not interfere with its stepping function. In summary, the above-mentioned single-molecule fluorescent labeling and tracing technology reveals the behavioral characteristics of motor proteins from the molecular level, enriching the basic theoretical research of molecular motors, and the related results are published in "CELL". Figure 1. Walking pattern of dynein on the microtubule skeleton (Spudich JA, Cell 2006) Fig. 2 Stepping behavior of quantum dot-labeled dynein on microtubule skeleton Source of the document: Reck-Peterson SL, Yildiz A, Carter AP, Gennerich A, Zhang N, Vale RD. Single-molecule analysis of dynein processivity and stepping behavior. Cell. 2006;126(2):335-48.
Plant extracts refer to substances extracted or processed from plants (all or a part of plants) using appropriate solvents or methods, and can be used in the pharmaceutical industry, food industry, daily chemical industry and other industries.
There is a conceptual overlap between plant extracts and herbal extracts. The raw materials of plant extracts in my country are mainly derived from Chinese herbal medicines, so domestic plant extracts can also be called Chinese medicine extracts to some extent.
Herbal Extract,Liquid Herbal Extracts,Herbal Extract Powder,Natural Herbal Extract XI AN RHINE BIOLOGICAL TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD , https://www.xianrhinebiotech.com