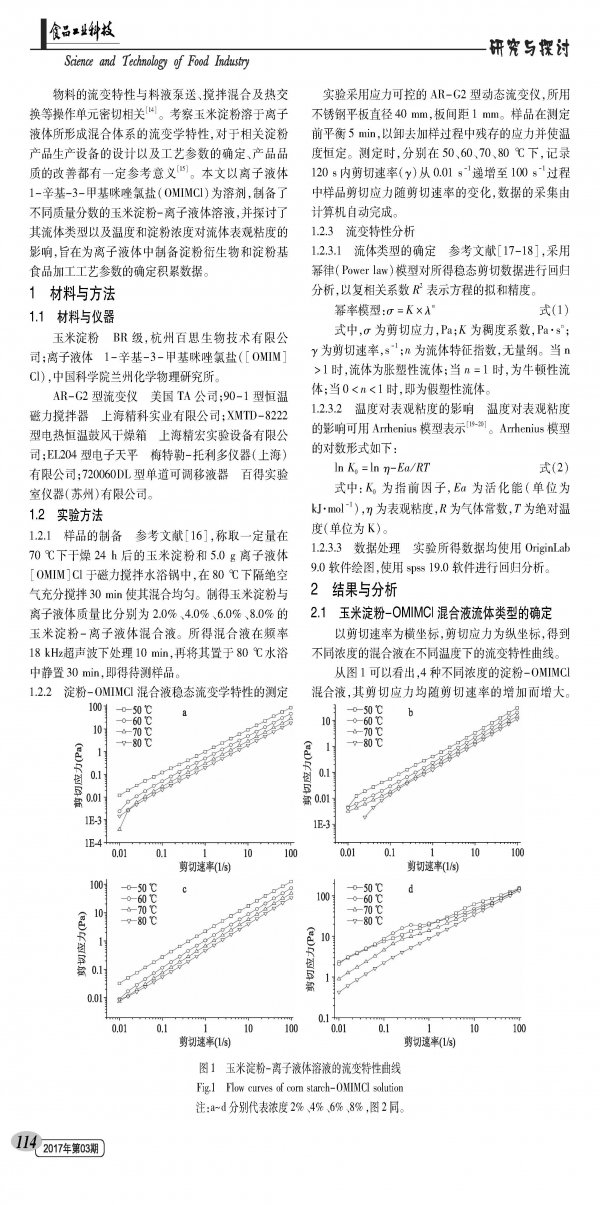
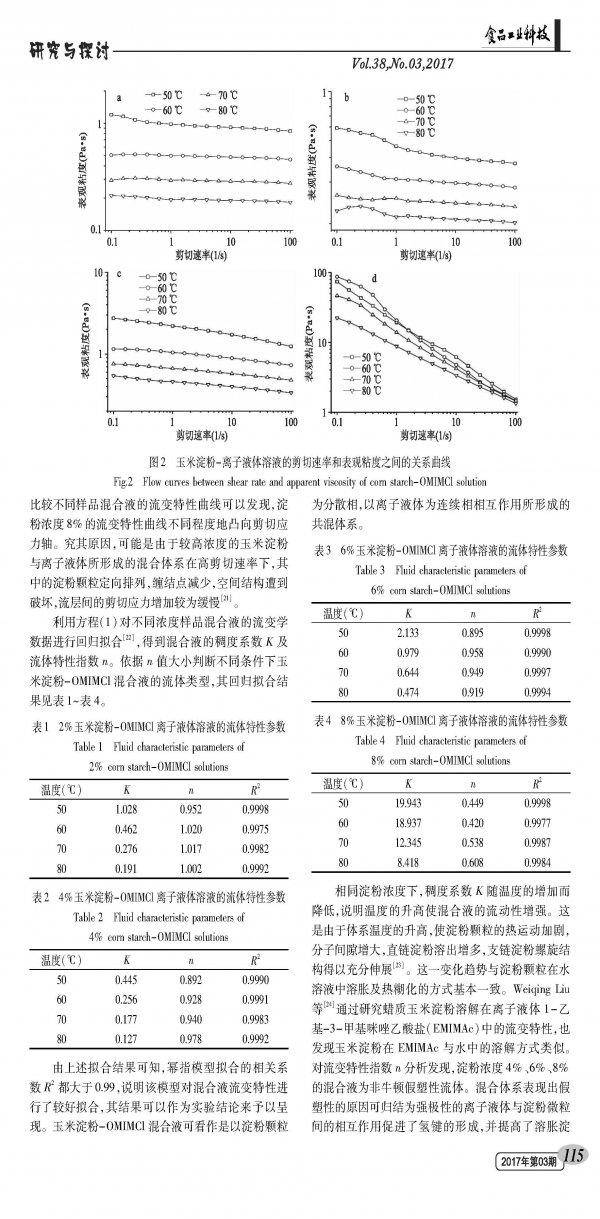
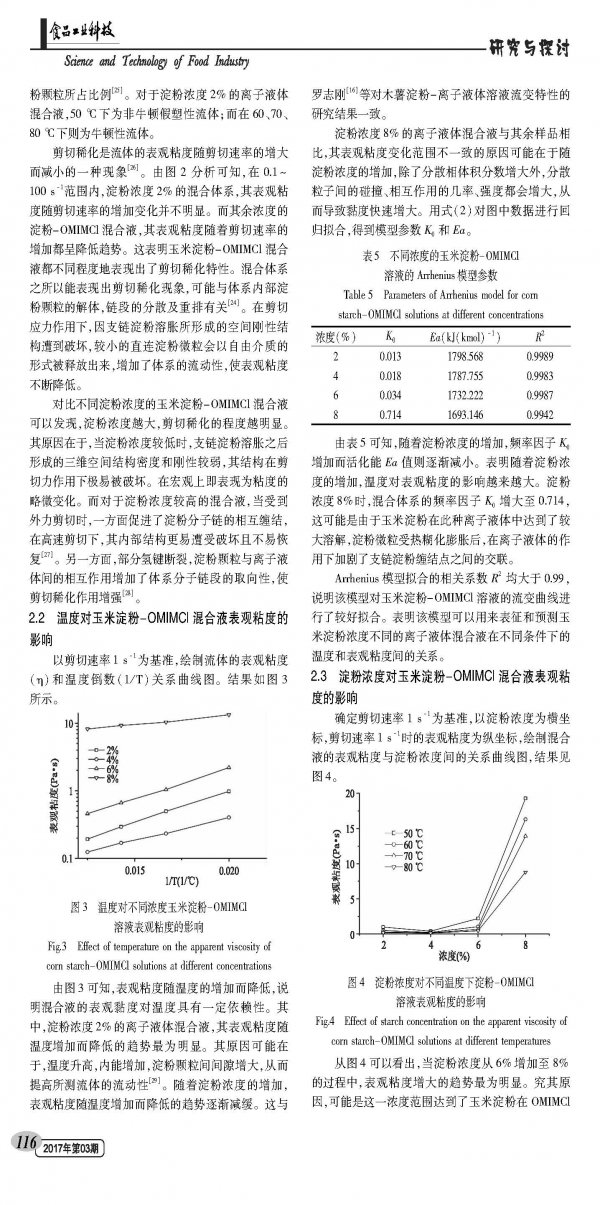
Starch is a kind of plant polysaccharide synthesized in liquids during photosynthesis of green plants. As an essential material for food processing, starch greatly increases the variety of product processing routes and food types. Due to its low gelatinization temperature and non-returnable properties and a wide range of sources, corn starch has become one of the hotspots of the current food industry. However, the problem of high solubility of corn starch has always been a major problem in starch-based food research. Since starch is difficult to disperse into a uniform and stable system in an aqueous solution, this causes problems such as poor reaction uniformity and low product substitution degree, and the organic solvent used in the conventional method has a large negative influence on product quality and environment. Ionic liquids are a type of molten salt system formed by ions which has been found to be liquid at room temperature in recent years. It is difficult to volatilize, difficult to oxidize, has high thermal stability, can be recycled, and most importantly, it has good solubility to most natural polymer compounds. In recent years, many scholars at home and abroad have studied the solubility characteristics of starch polysaccharides, cellulose and other plant polysaccharides in ionic liquids and the physicochemical properties of blends. Swatloski first reported in 2002 that ionic liquid [BMIM]Cl can dissolve cellulose and compare the effects of different structured ionic liquids on cellulose solubility. In 2013, Xu Yupeng et al studied the solubility of cellulose in the ionic liquid 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ([AMIM]Cl). The results showed that cellulose did not undergo derivatization during the dissolution process. Reaction. For starch polysaccharides, David et al. compared the solubility characteristics of rice starch, wheat starch, potato starch and the like in ionic liquid ([BMIM]Cl). The rheological properties of the material are closely related to the operating units such as feed pumping, mixing and heat exchange. Investigating the rheological properties of corn starch dissolved in ionic liquids, it has certain reference significance for the design of related starch product production equipment, the determination of process parameters and the improvement of product quality. In this paper, different mass fractions of corn starch-ionic liquid solutions were prepared by using ionic liquid 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride (OMIMCl) as solvent. The fluid type and temperature and starch concentration were also discussed. The effect of viscosity is intended to accumulate data for the determination of process parameters for the preparation of starch derivatives and starch-based foods in ionic liquids.