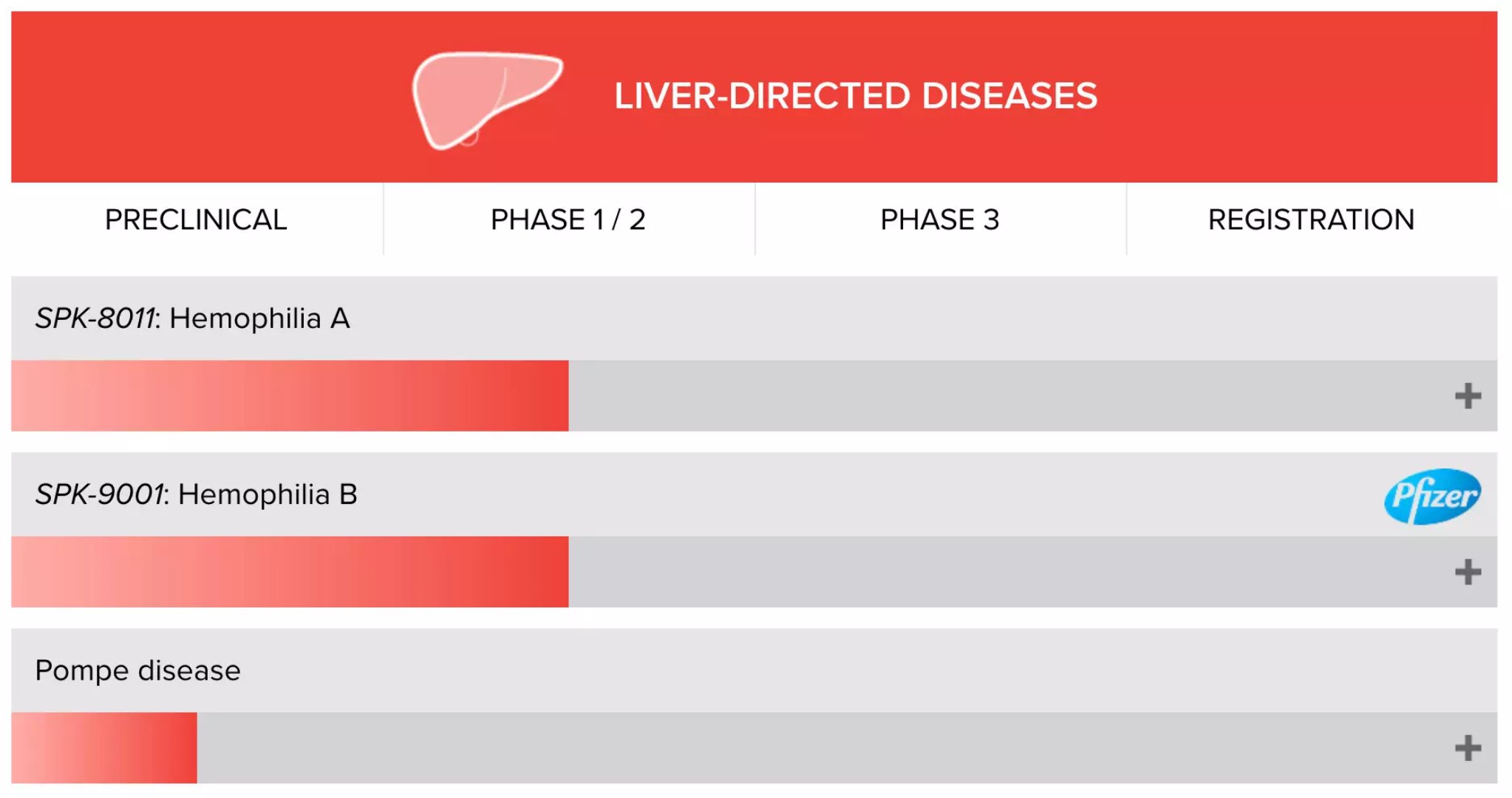
Gene therapy is expected to overcome hemophilia B, reducing the annual bleeding rate by 98% May 23, 2018 Source: WuXi PharmaTech Today, Spark Therapeutics and Pfizer announced that after a cumulative follow-up of more than 18 patient years (5 to 121 weeks), all 15 moderate to severe patients who are participating in the 1/2 phase clinical trial of the new drug SPK-9001 Patients with hemophilia B have discontinued conventional infusion of Factor IX concentrate. As of May 7 this year, all 15 patients had no serious adverse events and no thrombotic events or factor IX inhibitors. These data were published at the World Federation of Hemophilia (WFH) World Congress. Hemophilia B is a rare X-linked recessive disorder. Mutations in the gene encoding Factor IX resulted in a significant decrease in factor IX levels in vivo. This can lead to a decrease in the patient's coagulation function, which is a common symptom of the patient. Before the onset of effective therapy, severe hemophilia patients often did not live to adulthood, with an average life expectancy of only 11 years. The main treatment for hemophilia today is to supplement the blood deficiencies in the blood by regular infusion. This treatment can increase the life expectancy of hemophilia patients to only 10 years less than normal. However, it requires regular infusions from patients to control internal bleeding, which becomes a burden on their lives. Spark seeks to change this situation through gene therapy. SPK-9001, developed by the company in collaboration with Pfizer, is an adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector designed using bioengineering technology and contains a codon-optimized highly active human Factor IX gene. This vector is capable of expressing highly active Factor IX in the liver after introduction into the body by intravenous infusion. The therapy was approved by the FDA for breakthrough therapy. ▲Spark Therapeutics hemophilia research and development product line (Source: Spark Therapeutics official website) Based on the history of the study participants' previous year, the overall annual bleeding rate (ABR) of all 15 participants was reduced by 98% (based on data after 4 weeks; 97% based on post-infusion data), equivalent Each participant bleeds 0.2 times a year, compared to 8.9 before treatment. Only one participant had a bleeding episode after at least 4 weeks of infusion at SPK-9001. In this development-labeled, non-randomized, multicenter, phase 1/2 clinical trial, the overall annual infusion rate was reduced by 99% for all 15 participants (based on data after 4 weeks; calculations based on data after infusion) 99%), equivalent to 0.9 infusions per participant per year, compared to 57.2 before the infusion. Among them, 6 participants received factor IX after SPK-9001 administration: 2 reported spontaneous bleeding, 2 received infusion before surgery, 1 decided to infuse at the end of the study, and 1 was used to prevent mild A traumatic non-bleeding event. As of May 7, the data was at least 12 weeks after the SPK-9001 infusion - this is the time required to reach the level of Stable IX activity, and all 13 participants achieved more than 12% of the Factor IX stability level. The level of factor IX stabilizing activity in the top 10 participants from 12 weeks to 52 weeks of follow-up ranged from 14.3% to 76.8%. Participant IX stable activity levels for 3 participants of SPK-9001 using the enhanced process ranged from 38.1% to 54.5% during at least 12 weeks of follow-up. “We are pleased to see that all 15 participants, especially the top four participants who have been followed for more than two years, continue to show that a single administration of SPK-9001 can result in significant bleeding reduction and a reduction in factor IX infusion without serious "Our adverse events," said Dr. Katherine A. High, President and R&D Director of Spark. "Our commitment to gene therapy research for the entire hemophilia project remains unwavering. The goal is to develop a new treatment and bring A positive benefit risk profile to liberate patients who need regular infusions while eliminating spontaneous bleeding." Currently, Spark has completed the recruitment of SPK-9001 in a phase 1/2 clinical trial of hemophilia B, and plans to complete the transition to Pfizer this summer. In addition, Spark will deliver a batch of drugs to Pfizer for Phase 3 clinical trials. We look forward to the continued success of this new drug in follow-up trials, bringing innovative treatments to hemophilia patients as soon as possible. Reference materials: [1] Spark Therapeutics and Pfizer Announce Data from 15 Participants with Hemophilia B Showing Persistent and Sustained Factor IX Levels with No Serious Adverse Events [2] Hunting a cure, Spark reports steady progress on hemophilia B gene therapy as Pfizer preps for pivotal handoff
The RNA purification kit is used to purify and recover RNA molecules transcribed in vitro and total RNA extracted from various materials, which can effectively remove contaminating impurities in RNA samples. The recovery rate of this product can reach 80%, and the OD260/OD280 ratio of the obtained RNA is generally about 2.0, which can be directly used in subsequent sensitive experiments (such as microarray analysis, fluorescence RT-PCR, etc.). With the deepening of transcriptomics, the complexity of RNA types, expression regulation and functions is far beyond our imagination. Covid-19 Nucleic Acid Extraction Reagent,Nucleic Acid Extraction Reagent Kits,Dna Purification Kit,Rna Purification Kit Jilin Sinoscience Technology Co. LTD , https://www.jlgkscience.com

Removing ribosomal RNAs that account for more than 80% helps to focus sequencing on less abundant but informative RNAs. At present, the removal of rRNA is mainly through the combined use of probe and RNase H. The processed RNA will be mixed with many digestion products, enzymes and ions, which is not conducive to the subsequent construction of RNA library. Take the Columnar RNA Purification Kit as an example. Trizol is a ready-to-use reagent that can be used to purify total RNA from tissues and cells. This is a single-phase solution of phenol and guanidine isothiocyanate that facilitates lysis of tissues and cells, inhibiting RNases to maintain RNA integrity.