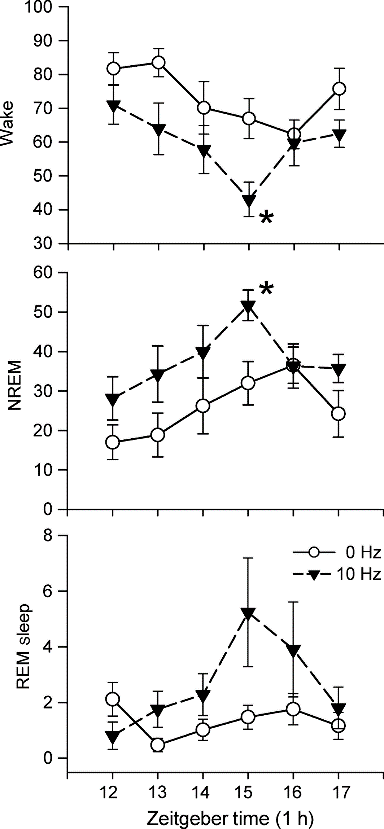
Optogenetics, also known as optical stimulation plus genetic engineering, is a technique for precisely controlling cell behavior in the brains of living animals through optical and genetic techniques. Due to its high temporal and spatial specificity, optogenetic techniques are widely used in the field of neuroscience. In 2010, optogenetics technology was awarded to Nature Methods Annual Life Science Technology. In 2010, it was considered by Science to be one of the breakthroughs in the past decade. The optogenetics technology was once again named by Nature Methods as one of the eight most noteworthy technologies of 2016. In the future, optogenetic techniques will contribute more to the treatment of diseases in the neurological and psychiatric fields and to the study of tissue functions beyond neuroscience. one. Before optogenetics       In 1979, Francis Crick suggested that there is an urgent need to develop a control technique in the field of neuroscience to manipulate certain cells in the brain without changing other conditions. Because the electrical stimulation signal can't accurately locate the cells, and the chemical drugs have a slow onset of action and cannot be precisely controlled, Crick considers whether light control technology can be used. Although microbiologists have long discovered that they can express visible light-gated proteins, no one has ever linked them at the time. Figure 1. Main research techniques in the field of neuroscience before the emergence of optogenetics two. Optogenetics 1. The development of optogenetics           In August 2005, an article published by Karl Deisseroth Lab brought a long-awaited new technology, optogenetics, to scientists in the field of neuroscience. The implementation of this technology is based on the discovery of a one-component control tool, the light-sensitive protein. Figure 2. The history of optogenetics 2. Principle of optogenetics          In neuronal cells, action potentials occur after depolarization of the cell membrane. Conversely, hyperpolarization of the cell membrane inhibits the appearance of a peak potential. By expressing an exogenous light-sensitive protein-encoding gene that changes the membrane potential in a neuronal cell, the peak-potential switch can be controlled by a light-controlled operation. Figure 3. Resting potential and action potential of neurons      The first of these microbial-encoded opsin neuron cell switches is ChR2 (channelrhodopsin-2). As a non-selective cation channel protein, ChR2 expressed in neurons immediately depolarizes neurons under blue light irradiation, inducing action potentials. However, scientists don't always want to activate neuronal cells. There is a test strain called NpHR, halorhodopsin, which is a chloride ion pump. When the neuron cells are irradiated with yellow light, super-chemical reactions occur to suppress the formation of action potentials. Figure 4. Photogenetic tools for regulating membrane potential - photochannel proteins (Erika Pastrana, 2011) 3. Auxiliary techniques and basic steps required for optogenetics The range of optogenetic techniques is extensive. It mainly includes the following. Figure 5. Photogenetics and its assistive technologies   In optogenetic manipulation, cells express a specific gene encoding a light-sensitive protein and then use light to alter the behavior of the cell. The basic steps of optogenetics to control cell function are as follows: Figure 6. Basic steps in optogenetics to control cell function     Among them, the method of transmitting the genetic information of the exogenous light-sensitive protein to the target cell by virus infection is the most convenient and quick. Thanks to the specific tissue tropism of adeno-associated virus (AAV) to the brain, AAV has become an important tool in optogenetic research . 4. The advantages of optogenetics technology - high spatial and temporal resolution     The optogenetics technology fundamentally solves the problem of how to precisely regulate cell behavior. This is based on its advantage of having a high degree of spatiotemporal specificity. The optogenetics technology can control the precision in milliseconds (ms) in time, and the spatial precision can reach a single cell level, which is unmatched by electrical signal stimulation and chemical drugs. Figure 7. High temporal resolution of optogenetics Third, ViGene provides you with a wide selection of AAV photochannel protein carriers      Specific promoters and specific AAV serotypes will provide more precise spatial localization for your photosensitivity experiments. ViGene offers you 24 promoters, 7 AAV serotypes and 5 light-sensitive channel proteins, over 840 vector combinations. In addition, you can customize the photo-sensitive vector plasmid according to your needs. A lot of choices make your personalized experiment needs!     Table 1. AAV serotypes provided by ViGene Cat.# Promoter Name Size Description Download AP10001 ALB 2.4kb Liver specific 10 timer stronger than CMV after 10 weeks Vector Sequence AP10002 GFAP104 845bp Hybrid of EF1a and GFAP Vector Sequence AP10003 CAG 944bp Strong promoter, ubiquitous expression in vivo Vector Sequence AP10004 CamKIIa 1.2kb Specific expression in excitatory neurons in the neocortex and hippocampus Vector Sequence AP10005 EF1A 1.2kb Ubiquitous, weaker than CMV but better for in vivo Vector Sequence AP10006 CK1.3 1.1kb Vector Sequence AP10007 CK0.4 217bp Calcium/Calmodulin-dependent kinase II alpha Vector Sequence AP10008 GFAP 1.0kb Specific in astrocyte Vector Sequence AP10009 MBP 1.3kb Myelin basic protein promoter, efficient transduction of oligodendrocytes by adeno-associated virus type 8 vectors Vector Sequence AP10010 EFFS 253bp A short version EF1A Vector Sequence AP10011 TBG 460bp Homo sapiens serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade A Vector Sequence AP10012 aMHC 0.4kb Mouse myosin heavy chain alpha promoter Vector Sequence AP10013 cTNT 702bp Specific transduce cardiomyocytes Vector Sequence AP10014 Synapsin 471bp Specific in neuron Vector Sequence AP10015 Mecp2 230bp Truncated Mcep2 neuron specific Vector Sequence AP10016 C-fos 1.7kb Activity-dependent promoter Vector Sequence AP10017 ApoE/AAT1 1.4kb Chimeric promoter of human alpha-1-antitrypsin and cer/hepatic locus control region (HCR). Liver specific. Vector Sequence AP10018 UBC 1.1kb Ubiquitous, weaker than CMV but better for in vivo Vector Sequence AP10019 PGK 400bp Ubiquitous, weaker than CMV but better for in vivo Vector Sequence AP10020 Somatostat 1.2kb Restricting expression to GABAergic neuron Vector Sequence AP10021 Rpe65 700bb Retinal Pigment epithelium-specific expression in vivo and in vitro Vector Sequence AP10022 Insulin1 1.0kb Specific in beta- cells of the pancreas Vector Sequence AP10023 3Xenhancer McK 728bp Much stronger than CMV in muscle, inactive in nonmuscle cell lines and mouse liver Vector Sequence AP10024 NSE 1.3kb Neuron-specific enolase promoter Vector Sequence Table 2. Promoter types provided by ViGene Table 3. Photosensitive channel protein types provided by ViGene Table 4: ViGene partial optogenetic spot Attachment: Literature related to optogenetics 1. Application of activated photochannel protein     In 2015, Dheeraj Pelluru et al. published an article in the European Journal of Neuroscience entitled Optogenetic stimulation of astrocytes in the posterior hypothalamus increases sleep at night in C57BL/6J mice, which was found to stimulate the hypothalamus during the active phase of the sleep-wake cycle. Astrocytes cause sleep, revealing the important role of astrocytes in the regulation of sleep-wake. Figure 1. ChR2-EYFP was specifically expressed in astrocytes by AAV5 . (Dheeraj Pelluru, 2015) Figure 2. Effect of different light stimulation frequencies on astrocytes to sleep. In the first 6 hours after turning off the lights, Using optogenetic techniques to activate astrocytes using different frequencies of blue light (473 nm, 10 ms), respectively Record the time of arousal, non-rapid eye movement sleep, and rapid eye movement sleep. It was found that a star expressing ChR2 was stimulated using 10 Hz. Glial cells can significantly increase the time of non-rapid eye movement sleep and rapid eye movement sleep, and reduce awakening accordingly between. (Dheeraj Pelluru, 2015) Figure 3. Effect of different light stimulation times on astrocytes to sleep. Starting at the 12th hour after turning off the lights, Activation of astrocytes using luminescence using different frequencies of blue light (473 nm, 10 ms) using optogenetic techniques for 1 min, Pause for 4 minutes for 6 hours to record the time of arousal, non-rapid eye movement sleep and rapid eye movement sleep. Found different time The stimulation between the awakening time and the non-rapid eye movement sleep time has a significant effect and peaks in the 15th hour after the light is turned off . (Dheeraj Pelluru, 2015) 2. Application of inhibitory photochannel proteins  In 2013, Michael T. Stefanik et al. published an article in Front Behav Neurosci entitled Optogenetic dissection of basolateral amygdala projections during cue-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking, which was discovered by inhibiting amygdala neurons and projecting to the central nucleus of the nucleus accumbens. The prefrontal cortex can reduce the possibility of recovery of cocaine in rats. Figure 4. Specific expression of ArchT in the lateral nucleus of the amygdaloid nucleus by AAV2. It was found that inhibition of neuronal activity by light can reduce the search for cocaine. The possibility of behavioral recovery. (A) Inhibition of amygdala neurons by 561 nm illumination can significantly reduce the number of active compression bars in rats; (B) DAB staining shows Overexpression of ArchT-GFP in amygdala neurons; (C) inhibition of amygdala neurons by light to reduce the effect of seeking cocaine, significantly superior In the absence of light, and close to the effect of subtractive administration; (D) illumination of AAV2-infected amygdala neurons with GFP only No impact. (Michael T. Stefanik, 2013) Figure 5. By inhibiting the projection of amygdala neurons to neurons in the central nucleus of the nucleus accumbens, the potential for recovery from cocaine behavior can be reduced. (A) Inhibition of central nucleus neurons in the nucleus accumbens by 561 nm illumination can significantly reduce the number of active compression rods in rats; (B) DAB staining is shown in Central nucleus accumbens region ArchT-GFP showed high expression; (C) by light irradiation inhibiting central nucleus accumbens reduce cocaine seeking obtained Effect, the effect is not significantly better than the acceptable light, and close to the reduction effect obtained by the administration. (Michael T. Stefanik, 2013) Figure 6. By inhibiting the projection of amygdala neurons on prefrontal neurons, the potential for recovery from cocaine behavior can be reduced. (A) Prefrontal neurons by inhibiting 561nm light, can significantly reduce the number of active lever in rats; (B) DAB staining display Prefrontal region ArchT-GFP showed high expression; (C) decreased prefrontal area sought to be obtained by light irradiation inhibiting cocaine The effect is significantly better than the effect of not receiving light , and is close to the effect obtained by subtractive administration. (Michael T. Stefanik, 2013) Figure 7. Schematic diagram of the location of the fiber optic terminal in the experiment. The number indicates the number of millimeters (mm) from the coronal section of the front chimney. (A) AAV injection of amygdala , located in the fiber end position of the amygdala; (B) AAV injection of amygdala, located in the voltazone The fiber end position of the nuclear central core; (C) the position of the fiber end position of the prefrontal lobe after AAV injection of the amygdala. (Michael T. Stefanik, 2013) Related Links:    Adeno-associated virus (AAV) service
The material of this scar sticker consists of a silicone gel, usually skin-colored in appearance, and is indicated for scar recovery treatment and prevention.It is prohibited to be used before the wound has healed. Allergic reaction to silicone rubber material is prohibited. Car scar stickers prevent the scars from proliferation effectively, soften and smooth the scars effectively. Scar car sticker relieve pruritus and pain quickly. Scar removing sticker Moisturizing and breathable, realistick scars sticker is reusable and washable; Comfortable, ultra-thin fabric,Safe and effective; scar patch sticker without latex and drug free; Before use this product, clean the scar area or wipe it with a cotton swab dipped in 75% alcohol to disinfect it before use, and let it dry. Open the package, remove lion king scar stickers and cut the scar patch to the right size. Remove the backing film and stick the sticky side on the scar. Blue scar silicone sticker can be continuously pasted on the scar surface until the stickiness disappears.
Scar Stickers,Fake Wound Stickers,Silicone Gel Dressing,Silicone Gel Scar Dressing Henan Maidingkang Medical Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.mdkmedical.com