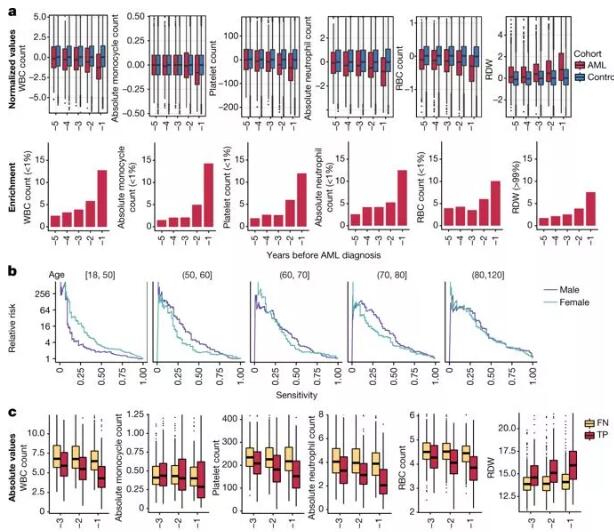
Release date: 2018-07-10 Today, Nature published a major study: a team of leukemia scientists from a number of scientific institutions around the world use blood tests and machine learning techniques to predict whether healthy individuals have acute myeloid leukemia (AML). )risks of. This study means that we can detect and monitor high-risk populations of AML early, and we can conduct research and development to find solutions to reduce the risk of the disease. Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a rapidly progressing, life-threatening blood tumor that affects people of all ages. Cancer cells in AML patients proliferate rapidly in the bone marrow and impede the production of normal blood cells, leading to bleeding and infection symptoms, and even life-threatening. In the past few decades, there has been almost no change in the mainstream treatment of AML. Although a small number of patients have been cured, this is still a terminal illness for the vast majority of patients. To reveal the cause of AML, the researchers used data collected from a large European population health and lifestyle study and blood samples to investigate. The large study tracked 550,000 people in 20 years, and some of them later developed AML. Using data from these people's blood samples, the researchers were able to review the genetic changes that exist in the blood of these patients a few years before AML appeared. The researchers developed a gene sequencing tool that sequenced blood DNA from 124 AML patients for known genes associated with AML and compared them with 676 people who did not have AML or related cancer. It is worth noting that they found that many genetic changes occurred in many people who later had AML, but not in those who did not. Moreover, those who later developed AML had more mutations in their genes, and these mutations also appeared more highly in their blood cells. Next, the researchers applied machine learning techniques to build an AML prediction model based on the usual record variables in the electronic health record. The model was able to predict AML within 6-12 months before diagnosis, with sensitivity and specificity of 25.7% and 98.2%, respectively. The model is consistent across different age groups. Schematic diagram of AML predictive model results constructed using machine learning techniques (Source: Nature) “In general, acute myeloid leukemia is a sudden onset,†said Dr. Grace Collord, one of the authors of the paper, from the Wellcome Sanger Institute and Cambridge University. “And this time we found that its cause is suffering. We were surprised to see that the disease was detected five years ago. This study provides a very important scientific basis for us to develop a program that can detect high-risk AML populations." The researchers also expressed the hope that based on the results of these studies, large-scale screening tests can be conducted to identify those at high risk of AML and to promote research to prevent further development of AML for the benefit of more patients. With the rapid development of artificial intelligence and the continuous advancement of medical technology, it is hoped that this research will bring us a new way to overcome leukemia in the future. Source: WuXi PharmaTech AI double chaise lounge,Chaise Lounges,leather lounge chaise Guangzhou LoPhiDa Co.Ltd , https://www.gdwidinlsa.com