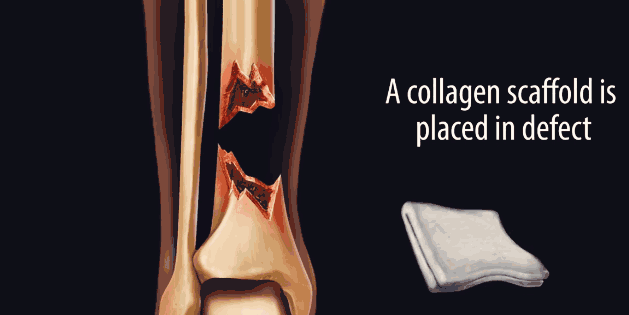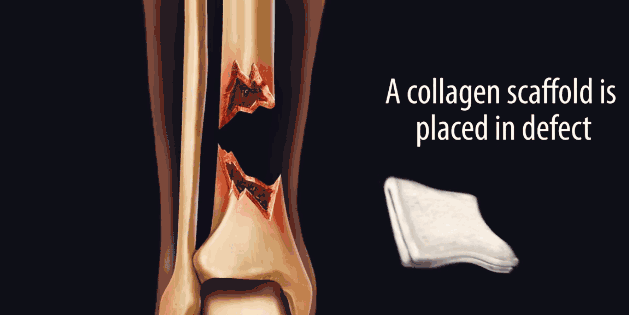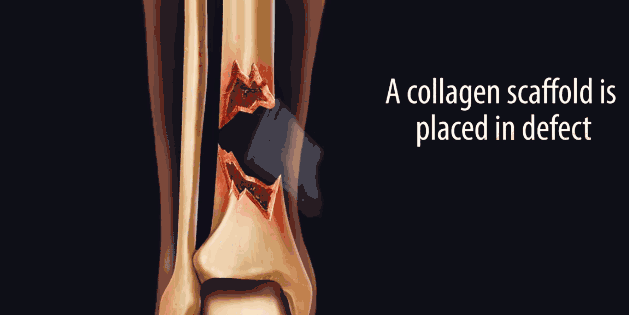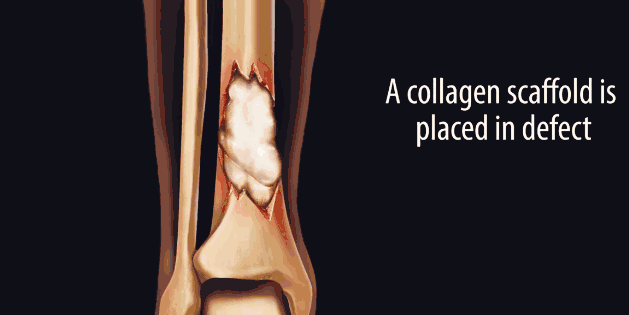
Fractures caused by falls in wars, car accidents, or elderly people with low bone density may result in incomplete healing of the bones and even lifelong disability due to excessive damage. People have been looking for ways to cure fractures. Now, the exploration has finally broken through, and the researchers combined the techniques of ultrasound, stem cells and gene therapy to repair and regenerate bone damage. Although this technology is currently only tested on animals, its performance in the upcoming human clinical trials is expected due to its excellent performance in the trial and excellent healing results. “This new study has significant clinical implications,†said David Kulber, director of plastic surgery at the Siddes Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles. "This technology that activates bone growth is very interesting." 丨David Kulber It is also worth noting that about 100,000 people in the United States are suffering from permanent bone damage caused by bone defects or bone fractures each year. In this case, the doctor usually performs bone grafting for the patient and transplants another bone tissue into the middle of the fracture. Ideally, the bone tissue used for transplantation is derived from the patient's own body—usually taking part of the humerus, and bone surgery is equivalent to a severe trauma, often making the patient “worse.†Therefore, the orthopaedic surgeon turned to obtain bones for bone grafting from the corpse. However, the sterilization step after bone removal from the cadaver destroys many key proteins and other signaling molecules that promote bone growth, greatly reducing the chance of complete healing of the bone graft after bone grafting. Therefore, researchers have been hoping to replace bone grafting by regenerating bone. They first tried to fill a gap between the ends of the fracture with a "natural scaffold" protein, collagen. Collagen will induce stem cells that differentiate into bones in the human body - mesenchymal stem cells migrate to the fracture gap for further differentiation. But in fact, mesenchymal stem cells do not specifically differentiate into bone cells. As a pluripotent stem cell, it may also differentiate into adipose tissue or scar tissue. For many years, researchers have been working to explore ways to differentiate mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts. To this end, they attempted to expose mesenchymal stem cells to different types of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), a class of growth factors that induce mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into bone tissue. Mesenchymal stem cells need to be exposed to BMPs for about a week to complete the differentiation process, while BMPs injected at the site of the fracture site have only a few hours of effective time. One injection is far from stimulating bone tissue regeneration. Baby Squid,Baby Octopus,Poulp Squid,Squid Tube GOLD STAR FISHERY ZHOUSHAN CO.,LTD. , https://www.goldstar-aquatic.com