Lancet Neurol: Can post-recovery VR technology for stroke patients bring a new gospel?
The application of virtual reality (VR) technology in the medical field has been in short supply. Recently, a study once again explored the possibility of this emerging technology in stroke rehabilitation. Can this high-end therapy bring new changes to the recovery of stroke patients?
In May 2016, the US AHA/ASA released the first adult stroke rehabilitation guide. One of the IA-level evidences suggested that patients should provide an abundance environment to participate more in cognitive activities and enumerate relevant research. The virtual reality (VR) game is proposed to improve the memory and attention of patients.
Recently, researchers from Canada, Gustavo Saposnik and others, have re-examined this technology from the perspective of recovery of motor function. The findings were published in the Lancet Neurology Journal. [Lancet Neurol 2016 Jun 27]
VR game vs simple entertainment
Non-immersive virtual reality is an emerging strategy for the recovery of motor function in stroke patients. Although this technology has rapidly spread in the field of stroke rehabilitation, evidence of the safety and efficacy of the technology is still limited. To further confirm the safety and efficacy of VR therapy, researchers have conducted research.
The Non-Immersive Virtual Reality Safety and Effectiveness for Stroke Rehabilitation (EVREST) ​​study was a randomized, single-blind, parallel-group trial that was completed between May 12, 2012 and October 1, 2015. The investigators included 141 patients from 14 stroke rehabilitation units in Canada, Argentina, Peru, and Thailand, aged between 18 and 85 years, who were the first to moderate ischemic stroke with mild to moderate upper extremity dyskinesia. The upper extremity score for exercise dysfunction within 3 months after random enrollment was 3 or more (evaluated using the Chedoke-McMaster scale).
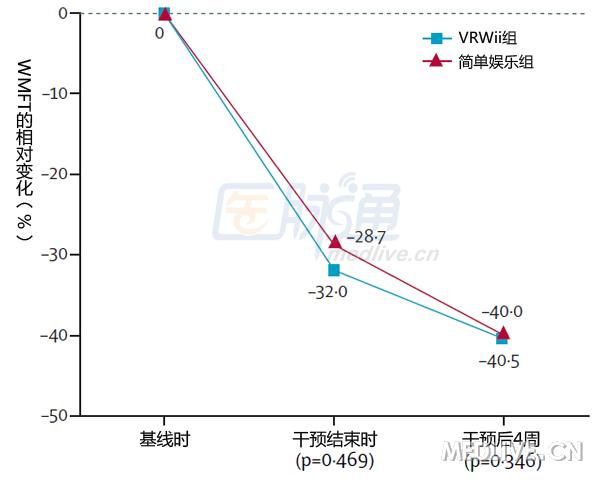
Participants were randomly assigned to the simple entertainment group (70 cases) and the non-immersive VR group (71 cases) for carding, bingo, building blocks, ball games or Nintendo Wii game system (VRWii) entertainment. Additional items for routine rehabilitation. The patient's recreational activities were structured, task-oriented upper limb training, completing 10 groups of 60 minutes each in 2 weeks. A total of 121 patients (62 in the simple entertainment group and 59 in the VR group) were evaluated.
The primary endpoint of the study was the patient's upper limb motor function. At the end of the 2-week dry expectation, the Upper Limb function was tested by the Wolf Exercise Function Test (WMFT) and the total length of time to complete the test was used as a measure of the primary end point of the study.
Is high technology "invincible"?
The results of the study showed that the motor function of both groups improved compared with baseline, and the median time to complete WMFT was shortened in both groups, and the difference was not significant. There was no significant difference in the mean time to regular rehabilitation between the two groups during the study period. After adjusting for baseline WMFT scores, gender, age, stroke severity, and other factors, there was no significant difference in the primary endpoints between the two groups.
There were 3 serious adverse events during the study, but they were not related to the intervention itself. The incidence of adverse events and serious adverse events was similar between the two groups.
It can be seen that for post-stroke patients with mild to moderate upper extremity dyskinesia, non-immersive VR as an additional treatment for conventional rehabilitation is not superior to ordinary recreational activities.
Researchers believe that post-stroke patients' motor rehabilitation may be less relevant to the type of task, as long as the task is sufficiently intensive and the task is scheduled for the patient. Compared to innovative VR technology, simple, low-cost common entertainment activities may be equally effective.
High quality cosmetics raw materials extraction technology was considered very important in the process of production, cosmetics is direct contact with our skin, so it is very important to cosmetics raw material quality and the quality, we can provide high purity cosmetics raw material, we have professional production equipment and professional production experts, in the cosmetics industry raw material supply, we have enough experience, Our company has 20 years of raw material export experience, and the company has a professional laboratory, professional equipment, testing center, to ensure the supply of high quality Cosmetic raw materials, cosmetic raw materials are processed through a certain proportion of various raw materials, can be generally divided into two categories: matrix raw materials and auxiliary raw materials. Our cosmetic raw materials mainly include:Cosmetic Raw,Cosmetic Phenylethyl Resorcinol,Isotretinoin Package Insert Pills,Organic Chlorella Powder
Cosmetic Raw,Cosmetic Phenylethyl Resorcinol,Isotretinoin Package Insert Pills,Organic Chlorella Powder
Xi'an Henrikang Biotech Co.,Ltd , https://www.henrikangbio.com